Back in .NET Conf 2017 The Xamarin team already shared what’s going to be new with Xamarin Forms 3.0 and it actually surprised me. I was expecting some performance improvements, bug fixing and a big upgrade on XAML. But, what they announced focuses on enabling the usage of Xamarin.Forms in more ways and on more platforms. I was really hoping for XAML improvements, maybe add some cascading styling like how CSS works. Maybe sometime in the future, we’ll get it. For now, I’ll just use the XAMLCss by warapa. Anyway if you want to watch all sessions from .NET Conf 2017, you can check it out on Channel9. Going back, I really didn’t expect these new features, but definitely, I love it and really excited to try it out!
That’s why right now, I’m going to show to you one of the exciting features added to the Xamarin.Forms 3.0 that I think you’ll also love. I’m talking about Xamarin.Form’s macOS support.
Is there a specific reason why Xamarin doesn't support building Mac apps from Visual Studio on Windows, the same way it pairs to a Mac to compile for iOS projects? I'm glad there is a path with Visual Studio for Mac, but I find it less productive (time-wise) for me personally than when I'm writing iOS apps on Visual Studio in Windows then. Xamarin lets you develop fully native Mac apps in C# and.NET using the very same macOS APIs as you would for Objective-C or Swift projects. You can either create your user interfaces directly in C# code, or, thanks to Xamarin's direct integration with Xcode, you can use Xcode's Interface Builder.
One of the Xamarin team’s plan is to reach more platforms. That means UWP, iOS and Android are not only platform the Xamarin.Forms will be able to target from now on, they are also bringing macOS, GTK#, Linux and WPF!
You might think that it will be hard and will take a lot of time to integrate your Xamarin.Forms solution into the macOS project, but it’s not. Not at all. You’ll be able to create a native macOS application using your Xamarin.Forms solution using Visual Studio for Mac or Xamarin Studio in just 3 quick steps!
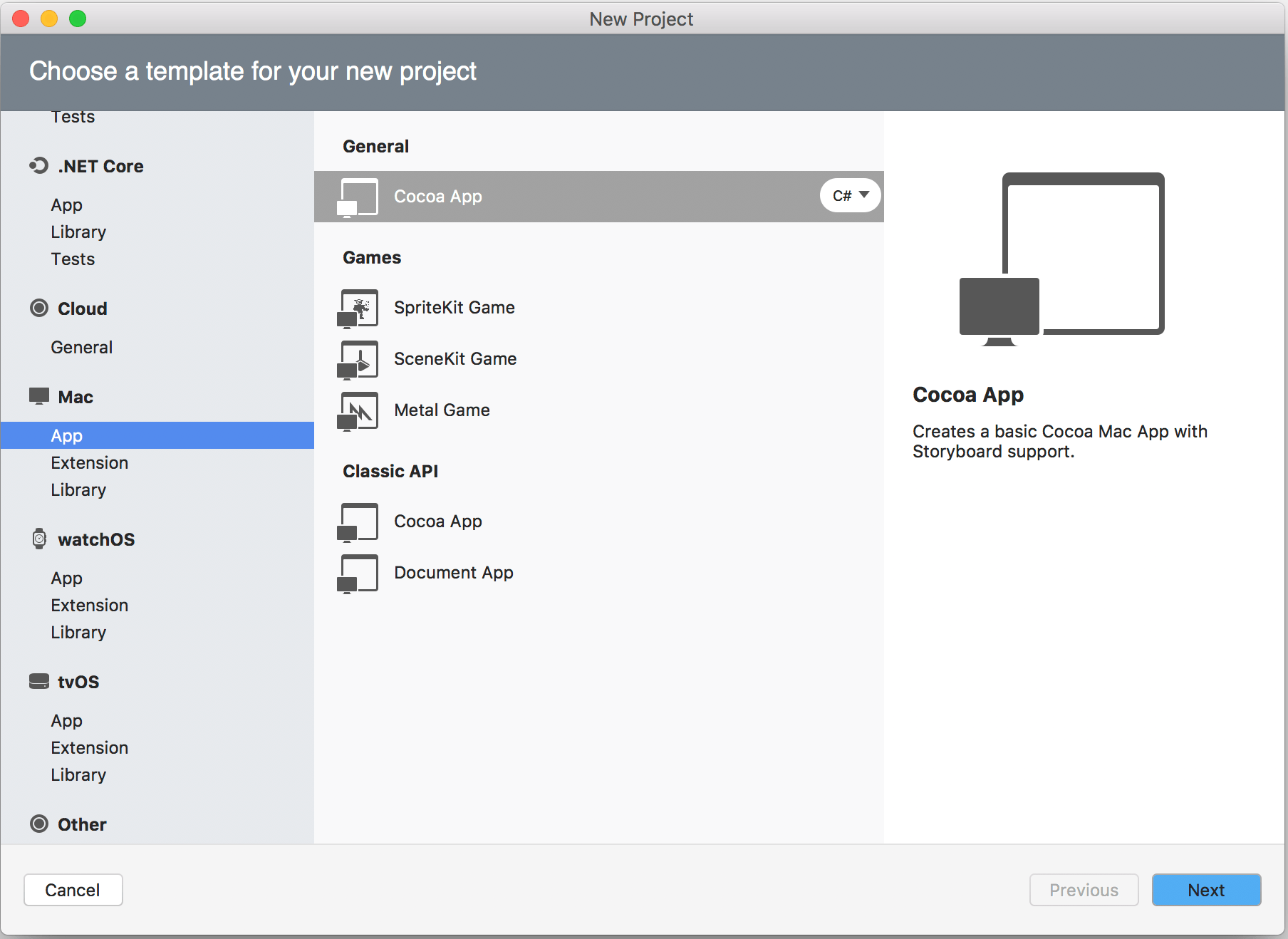
First step: Add a Cocoa App project
Right now, Xamarin.Forms template doesn’t have a Cocoa App initially. So, what you would do is to start Visual Studio for Mac or Xamarin Studio and open your existing Xamarin.Forms solution. Then, add a project into the solution by right-clicking the solution and selecting Add > Add New Existing Project.
You can then select Mac > App > Cocoa App and name it whatever you want, but ideally, the name has a suffix of .macOs.
Second Step: Add the Xamarin.Forms NuGet Package
You will have to add the Xamarin.Forms’ latest pre-release nuget package or specifically 2.4.0.282. To do this, right click the Cocoa App project that you just created and select Add > Add Nuget Packages.
Then, search for ‘Xamarin.Forms’ and make sure that the ‘Show pre-release packages’ is ticked. Click ‘Add’ to add Xamarin.Forms nuget package.
You will also need to update the Xamarin.Forms on your shared project and the version should be the same with what the Cocoa app have.
Third Step: Configure the Cocoa App Project
The first thing that you should do with your Cocoa app project is to add the shared project into your Cocoa app as a reference.
Then, open the Info.plist and remove the ‘Main storyboard file base name’ entry (Opened with XCode)
Or just open the Info.plist inside Visual Studio or Xamarin Studio by clicking it and leave the Main Interface blank.
The next one is to update your Main.cs’ Main method to initialize the AppDelegate:
Lastly, update the AppDelegate by changing the NSApplicationDelegate to FormsApplicationDelegate:
Initialize the Cocoa app window within the constructor:
Then inside the DidFinishLaunching method, initialize Xamarin.Forms and load the application:
You can now set your project as the startup project and run your macOS!
Again, in just 3 quick steps, it’s done!
This is just a basic walkthrough since this is still on preview. Expect that there are still bugs and not ready for production. Not all nuget packages are compatible and surely, there are lots of UI features still not implemented, but this is a good start. For now, you can send your issues and problems that you encounter in this forum discussion: https://forums.xamarin.com/discussion/93585/preview-xamarin-forms-for-macos/p1
JetBrains Rider supports creating and working with Xamarin applications for both Android and iOS. Although currently JetBrains Rider does not provide a designer or a previewer for Xamarin forms, you can still benefit from code analysis, coding assistance, and debugging features in C#, VB.NET, and other languages, as well as from general IDE features, such as the integrated VCS client.
If other tools that Xamarin relies on (for example, Android SDK, Android Emulator) are configured properly, you will be able to build and run your Xamarin application right from the JetBrains Rider IDE.
Xamarin SDK
To develop Xamarin Applications you need to have a Xamarin SDK on your machine. There are two different Xamarin SDKs — for iOS/Mac and for Android.
Xamarin SDK consists of two parts:
Assemblies with .NET types for the target platform. For example, a .NET type to represent the base OSX
NSObject. Using these assemblies, IDE and compiler resolve and build user code.Tools that transform .NET projects into native applications, which can be deployed and executed on the emulator or a physical device. For example, using these tools .apk packages for Android are built.
JetBrains Xamarin SDK
JetBrains Rider can use different Xamarin SDKs, for example the one from Visual Studio. However, if you do not have Visual Studio on your machine, you can use JetBrains Xamarin SDK prepared and packed by the JetBrains Rider team.
JetBrains Xamarin SDK is a custom build of Xamarin GitHub sources with some improvements and additional code.
Currently JetBrains Xamarin SDK lacks some features compared to Visual Studio Xamarin SDK, but it is in the process of constant improvement.
JetBrains Xamarin SDK is available for Windows and macOS:
There are two JetBrains Xamarin SDK builds available on Windows targeting the following platforms:
- Apple platform (iOS, Mac, tvOS, watchOS)
JetBrains Xamarin SDK for iOS development provides a limited feature set on Windows. For example, currently it does not supportconnecting to a remote Mac and perform full build/deploy.
JetBrains Xamarin SDK for Apple platforms on Windows ships as a .zip file (~ 60Mb) and installs into the JetBrains MsBuild directory:
%LOCALAPPDATA%JetBrainsBuildTools. - Android
JetBrains Xamarin SDK for Android development provides a solid feature set. However, fast deployment is currently not supported.
JetBrains Xamarin SDK for Android platforms on Windows ships as a .zip file (~ 700Mb) and installs into the JetBrains MsBuild directory:
%LOCALAPPDATA%JetBrainsBuildTools.
There are two JetBrains Xamarin SDK builds available on macOS targeting the following platforms:
- Apple platform (iOS, Mac, tvOS, watchOS)
On macOS, JetBrains Xamarin SDK for Apple platforms provides almost the same feature set as Visual Studio SDK, all known scenarios are supported.
JetBrains Xamarin SDK for iOS development on macOS ships as a .dmg file (~ 700Mb) and installs into:
/Library/Frameworks/Xamarin.iOS.framework
/Library/Frameworks/Xamarin.Mac.framework
/Library/Frameworks/Mono.framework/External
- Android
JetBrains Xamarin SDK for Android development provides a solid feature set. However, fast deployment is currently not supported.
JetBrains Xamarin SDK for Android development on macOS ships as a .dmg file (~ 700Mb) and installs into:
/Library/Frameworks/Xamarin.Android.framework
/Library/Frameworks/Mono.framework/External
Before you start
Xamarin aims to be executed on a variety of different platforms and therefore Xamarin development relies on several different tools for building and running your applications.
On Windows, you can develop Xamarin applications for any platform, but local build and run/debug is limited to Android devices and emulators.
If you use Visual Studio Xamarin SDK, you will be able to build and run your application on iOS and macOS. To do so, configure a Mac agent accessible on the network, and then connect to it (Tools | iOS | Xamarin Mac Agent).
Install a Xamarin SDK for iOS on your machine in one of the following ways.
Install Xamarin in Visual Studio. Note that you can use Visual Studio Community, which is free. If you already have Visual Studio installed, you have to add Xamarin support to it.
Start installation of Xamarin iOS & Mac on the Environment page of JetBrains Rider settings Ctrl+Alt+S and follow the installation wizard. This way JetBrains Rider will automatically download and install JetBrains Xamarin SDK for iOS & Mac.
Alternatively you can clone the Xamarin open-source repo from GitHub, build it and install on the machine. This way is quite complicated and we do not recommend it.
Install Android development tools in one of the following ways:
Start installation of Xamarin Android on the Environment page of JetBrains Rider settings Ctrl+Alt+S and follow the installation wizard. This way JetBrains Rider will automatically download and install JetBrains Xamarin SDK for Android.
Alternatively, all components that are automatically installed on the the Environment page of JetBrains Rider settings Ctrl+Alt+S, could be also installed manually:
Rider Xamarin Android Support plugin. It has all necessary features, like Android SDK manager.
Android SDK developed and provided by Google. You can install it from Visual Studio, Android Studio, Rider (with Rider Xamarin Android Support plugin), or downloaded as a set of command line tools.
On macOS, you can develop, build and run fully cross-platform Xamarin applications.
Install a Xamarin SDK on your machine in one of the following ways.
Install Visual Studio for Mac.
Start installation of Xamarin iOS & Mac on the Environment page of JetBrains Rider settings Ctrl+Alt+S and follow the installation wizard. This way JetBrains Rider will automatically download and install JetBrains Xamarin SDK for iOS & Mac.
Alternatively you can clone the Xamarin open-source repo from GitHub, build it and install on the machine. This way is quite complicated and we do not recommend it.
For iOS and Mac development, install Xcode. You will need an Apple ID for installing and signing into Xcode. If you do not already have it, you can create a new one at https://appleid.apple.com.
JetBrains Rider will detect Xcode automatically. If you have several Xcode versions, you can choose which one to use on the Build, Execution, Deployment | iOS page of JetBrains Rider settings Ctrl+Alt+S.Install Android development tools in one of the following ways:
Start installation of Xamarin Android on the Environment page of JetBrains Rider settings Ctrl+Alt+S and follow the installation wizard. This way JetBrains Rider will automatically download and install JetBrains Xamarin SDK for Android.
Alternatively, all components that are automatically installed on the the Environment page of JetBrains Rider settings Ctrl+Alt+S, could be also installed manually:
Rider Xamarin Android Support plugin. It has all necessary features, like Android SDK manager.
Android SDK developed and provided by Google. You can install it from Visual Studio, Android Studio, Rider (with Rider Xamarin Android Support plugin), or downloaded as a set of command line tools.
You can check the status of Xamarin tools and install or update them on the Environment page of JetBrains Rider settings Ctrl+Alt+S:
Create and open Xamarin projects
Xamarin For Mac Tutorial
JetBrains Rider supports creating new and working with existing projects. Project templates are available, too.
Xamarin For Mac
You can create a new Xamarin project in a new solution using File | New... or add a new Xamarin project to the existing solution by right-clicking the solution or solution folder node in the Solution Explorer, and choosing Add | New Project.
Xcode integration on macOS
When developing Xamarin applications on macOS, it is recommended to edit resource files and connect resources to code using Xcode.
You can use context menus of .storyboard, .xib, .plist files or of the Xamarin macios project node to open them in Xcode.
If the file or project has never been opened in Xcode before, JetBrains Rider will generate an Xcode project as follows:
xcodeproj project specifications (a project descriptor similar to csproj but for Xcode) is generated
Source files for all user types inherited
NSObject(forms, delegates, views, controls, and so on) in Objective C are generatedAll resources (images, designer files) are copied
When the project structure is ready, Xcode will start automatically and you can use it to edit resources. Every time Rider receives focus, it looks for changes (edits in existing files, new files, removed files) and integrates these changes into the Xamarin .NET project. It modifies .designer.cs parts of user types (inherited from NSObject) and copies back all changed resources.
All Xcode-related events are printed in the Xcode console tool window, which appears when you open resources or projects in Xcode:
When you create a new Xamarin macios project
JetBrains Rider creates the corresponding xcodeproj project (pbxproj and other necessary files) project in the objxcode subdirectory with all required settings and configurations.
Copies of all content files (views, plist files, images, and so on) are created in that directory.
For each
ViewControllertype JetBrains Rider generates an objc class with actions and outlets.The generated project is opened automatically in Xcode.
When you made changes in Xcode and then switch to Rider
All modified content files are copied back into .NET project.
Settings are updated.
objc files are parsed and *.designer.cs files are regenerated for view controllers. For all these files you will see a generated header:
// WARNING//// This file has been generated automatically by Rider IDE// to store outlets and actions made in Xcode.// If it is removed, they will be lost.// Manual changes to this file may not be handled correctly.
Run and debug Xamarin applications
When you create or open a Xamarin project, JetBrains Rider automatically creates run/debug configurations for each Xamarin project in the solution.
If you want to adjust something in the way your application starts and executes, you can edit and create new run/debug configurations. When you start a Xamarin application from the IDE, you can use the corresponding selector on the navigation bar to choose which configuration should be used:
Debug a Xamarin project, which was not created with JetBrains Rider
In the Settings/Preferences dialog Ctrl+Alt+S, select Environment.
Enable Xamarin Android and Xamarin iOS & Mac support.
If you are on Windows and have Xamarin SDK installed via Visual Studio, it will be detected automatically. Otherwise, JetBrains Rider will suggest installing JetBrains Xamarin SDK.
JetBrains Xamarin SDK cannot be installed alongside with Visual Studio Xamarin SDK.
Once Xamarin SDK is installed, you can create Xamarin-specific run/debug configurations.
Open the Run/Debug Configuration dialog in one of the following ways:
Select Run | Edit Configurations from the main menu.
With the Navigation bar visible (View | Appearance | Navigation Bar), choose Edit Configurations from the run/debug configuration selector.
Press Alt+Shift+F10, then press 0 or select the configuration from the popup and press F4.
In the Run/Debug Configuration dialog that opens, press Alt+Insert or click , then choose Xamarin.Android, Xamarin.iOS, or Xamarin.Mac from the list.
Specify the target project and other parameters if necessary, then click OK.
Use the newly created configuration to run and debug your Xamarin project.
Webinar recording: Better Xamarin Development with Rider for Mac
You can also watch this webinar recording where Dylan Berry explores the various ways Rider can help you improve your coding speed and quality when developing Xamarin apps.
Webinar agenda:
0:05 – Introduction
1:22 – Tools are important
11:00 – Get started with Rider on Mac
13:43 – Exploring Rider
1:04:46 – Plugins
Xamarin Android For Mac